
For example, if a publisher (for example a website) charges a CPM of $2, you will pay $2 for every 1,000 ads that its visitors see. Media buyers pay for every thousand impressions of an ad. It does not matter if an ad was clicked on or not. The CPM model is often used in native advertising. What is the CPM Model and How is It Calculated? An ad tracker such as Voluum allows you to track costs and profits using different methods ( S2S postbacks or pixels), connect different marketing channels and provide in-depth analysis, with metrics such as eCPM or eCPC calculated automatically. While most ad networks offer a rudimentary tracking solution, a dedicated tracker is a must for a seasoned marketer. The number one condition of using these cost models is to accurately track your costs and profits.

Every time a customer clicks on the ad, the advertiser pays publishers a fraction of their profits. Revshare ( Revenue Share) – this pricing model is based on the percentage payouts on the revenue made from offers.
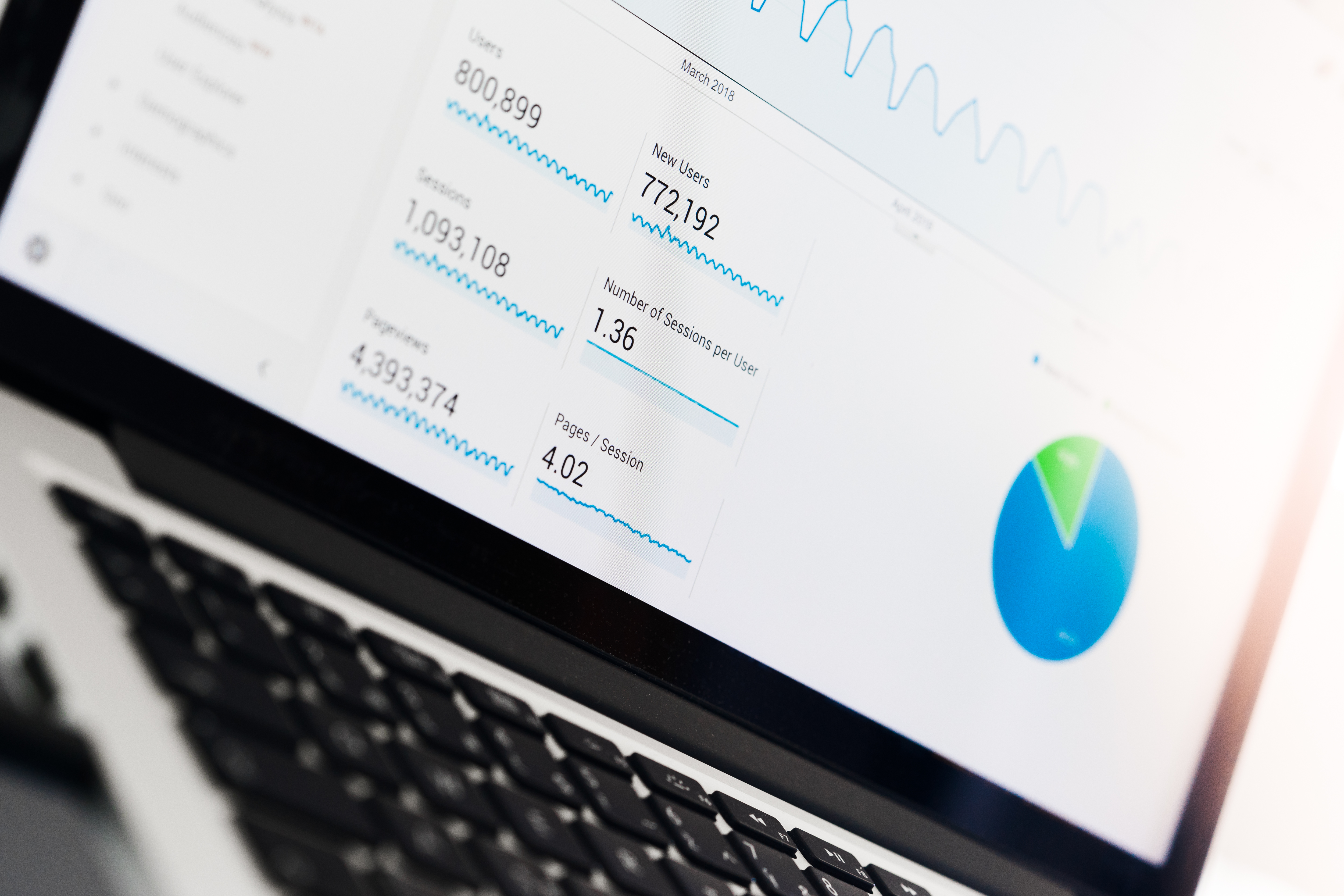
CPV ( Cost Per View) known as PPV ( Pay Per View) – a media buying model in which advertisers pay just for a single ad view on the publisher’s site.Advertisers pay whenever the app they are promoting gets downloaded and installed by a user who interacted with an ad. Essentially, it is like cost per acquisition (CPA), but just a bit more precise. CPI ( Cost Per Install) – this model is reserved for mobile app marketers.In this media buying model, advertisers pay when a lead form with some crucial user data is completed and submitted. CPL ( Cost Per Lead) – simply put, a type of CPA.This conversion may be any desired action on the website, like a sign-up or a purchase. CPA/CPS ( Cost Per Acquisition or Cost Per Sale) – in such a case, advertisers pay only if a conversion happens.CPC ( Cost Per Click), also known as PPC (pay per click) – in this revenue model the advertiser only pays whenever an ad is clicked on.It’s one of the most common ways of DSP media buying. So basically, every time an ad loads on a page or in an application. CPM ( Cost Per Mille) – a pricing model where the advertiser pays for a thousand impressions (ad views).Just make sure you understand the pricing models correctly. Then decide what will work best for your campaigns. Think about your product, your KPIs (Key Performance Indicators), and your target users.

And we’re here to help you identify that. Shocker, right?īut there’s always one that can be the best fit for you and your advertising. Types of Pricing ModelsĪll the models have their advantages and disadvantages. This is why we created this article – so you can learn about the most common pricing models and understand why the CPM model is almost always the best choice for native ads. We work with performance marketers quite often and at some point, we noticed that understanding pricing models can be difficult, especially at the very beginning.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
